Queueing jobs¶
Here’s a simplified workflow of queueing jobs to the supercomputer.
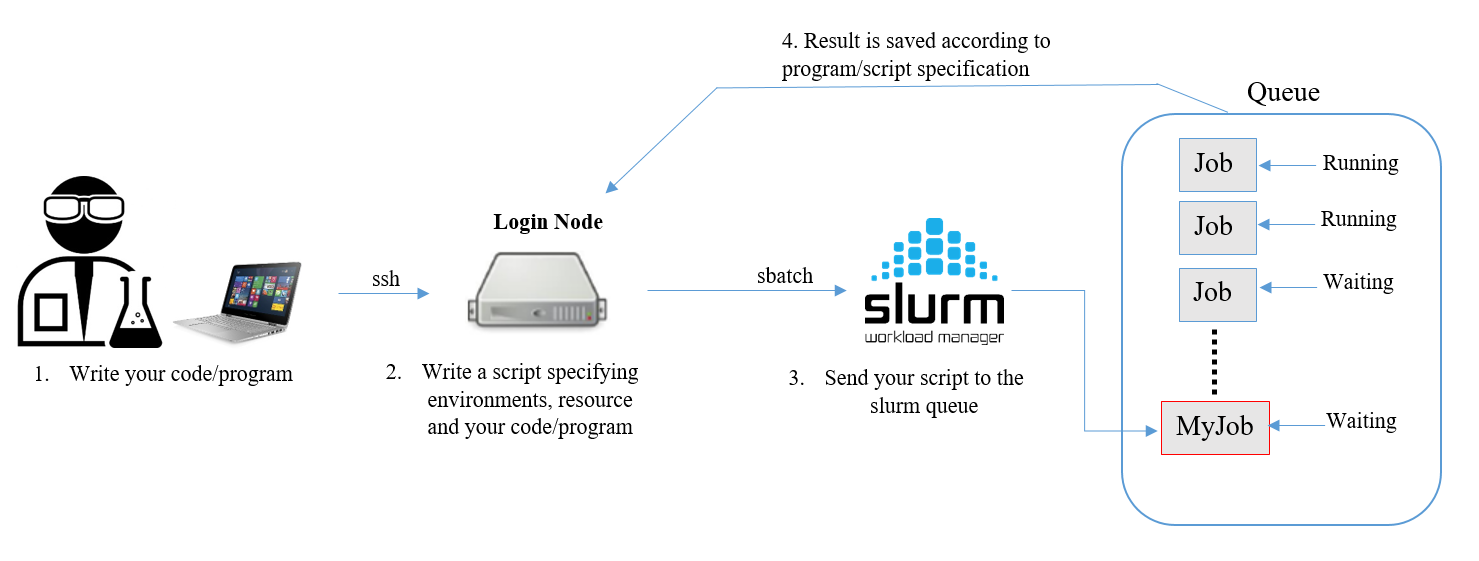
For running large time consuming programs, sending the job to the queue system is preferred.
-
You can submit a job script to the Slurm queue system from the login node with:
sbatch <filename>
By default any output messages from the job are written to the file
slurm-XXX.outwhereXXXis the job id. More information on how to create an job script can be found in Job scripts.
Warning
Note that programs should ONLY be run with sbatch, or following the instruction in Run interactively Running programs in any other way will result in the program running on the login node and not on the super computer.
-
You can remove your job from queue with:
scancel <jobid>
-
Information about the jobs running in the queue can be obtained with:
squeue -
You can also see your job in the queue by adding a flag:
squeue -u <username>
The state of job is listed in the ST column. The most common job state codes are:
-
R: Running
-
PD: Pending
-
CG: Completing
-
CA: Cancelled
For more job state codes please visit Slurm Job State Codes.
-
-
To get further information about your jobs:
scontrol show job <jobid>
-
To get detailed status information of a running job/step:
sstat --jobs=your_job-id
The sstat command displays information about CPU usage, task information, node information, Resident Set Size (RSS) and virtual Memory (VM).
By the default sstat outputs much more information than what is normally needed. However, this information can be filtered using the flag
--formattogether with a list of the fields we want to have. For example:sstat --jobs=your_job-id --format=JobID,aveCPU,MaxRRS,NTasks
-
To get detailed information on past jobs:
sacctThis command is very similar to sstat, but instead of pulling information from jobs that are currently running, it provides information on past jobs.
To get information on a certain job:
sacct --jobs=your_job-id
Jobs can also be queried using your username:
sacct --user=your_username
By default sacct show jobs executed after 00:00:00 of the current day. To search for older jobs user the flag
--starttime:sacct --starttime=YYYY-MM-DD
The output of sacct can be formated with the flag
--formatin the same manner than with sstat. The command can provide very detailed information, and thus, the list of possible fields that can be requested is long. Please use the flag--helpformator check the man page of sacct for more information.As an example, the following command would show information on jobs executed after June 23 2019. The information will contain job name, CPU time used, number of nodes used, maxrss, and elapsed time:
sacct --starttime=2019-06-23 --format=JobName,CPUTime,NNodes,MaxRSS,Elapsed
The full list of fields and an explanation for each one of them can be found by using the flag
--helpformator by visiting the man page for sstat. -
To get a view on nodes and partitions (logically-grouped nodes) offered by the cluster:
sinfo
More information on all these SLURM commands can be found on their respective man pages.