PerMedCoE@PDC
Alessandra Villa, PDC
PerMedCoE ( permedcoe.eu ) is the high-performance computing (HPC)/exascale centre of excellence (CoE) for personalised medicine in Europe. This CoE is working to provide an entry point to HPC/exascale methodology to translate omics analysis into actionable models of cellular functions. (“Omics” is an informal term covering the biological sciences that end in “omics”, such as genomics and proteomics.) The core software packages for these efforts are COBREXA.jl, CellNOpt, MaBoSS and PhysiCell.
The KTH Royal Institute of Technology is one of the partners in the CoE, and PDC has been contributing to building PerMedCoE and the associated HPC research community, as well as mapping competencies needed by professionals in the personalised medicine field, designing target training materials, running use cases and optimising the performance and scalability of PerMedCoE workflows.
In particular, over the last few months, PDC has worked on the development of a competency hub in the field of computational personalised medicine (which is hosted by EBI-EMBL) and also on developing training materials and occasionally on filling in the gaps between the fields of personalised medicine and HPC, and finally on evaluating the scalability and performance of PerMedCoE workflows.
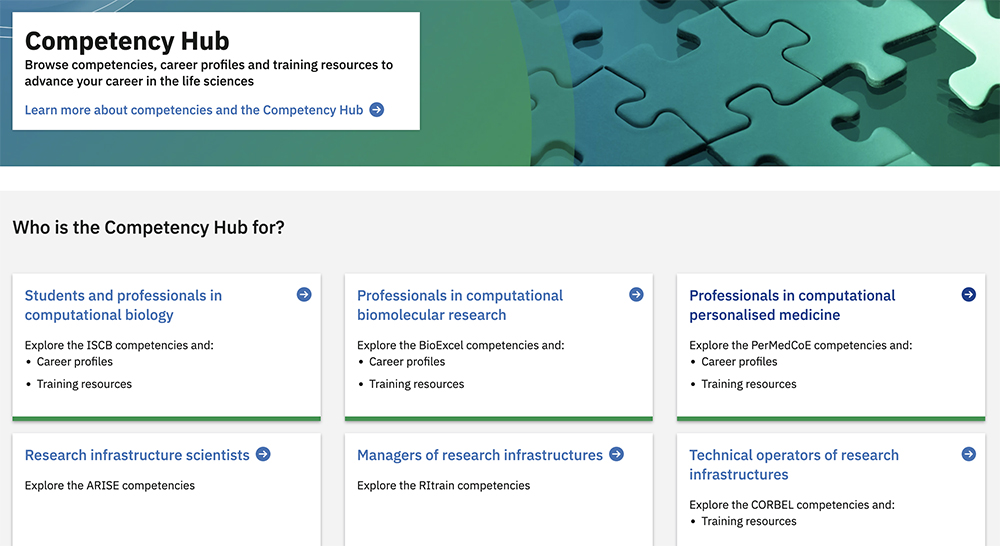
The competency hub ( competency.ebi.ac.uk ) is a hub where researchers can browse competencies, career profiles and training resources to advance their careers in the life sciences. PDC has identified and defined a series of competencies that professionals in the field of computational personalised medicine require for different career profiles and collected that information in the hub. Some examples are a postdoctoral fellowship in molecular dynamics simulations and a position as a senior researcher and software architect.

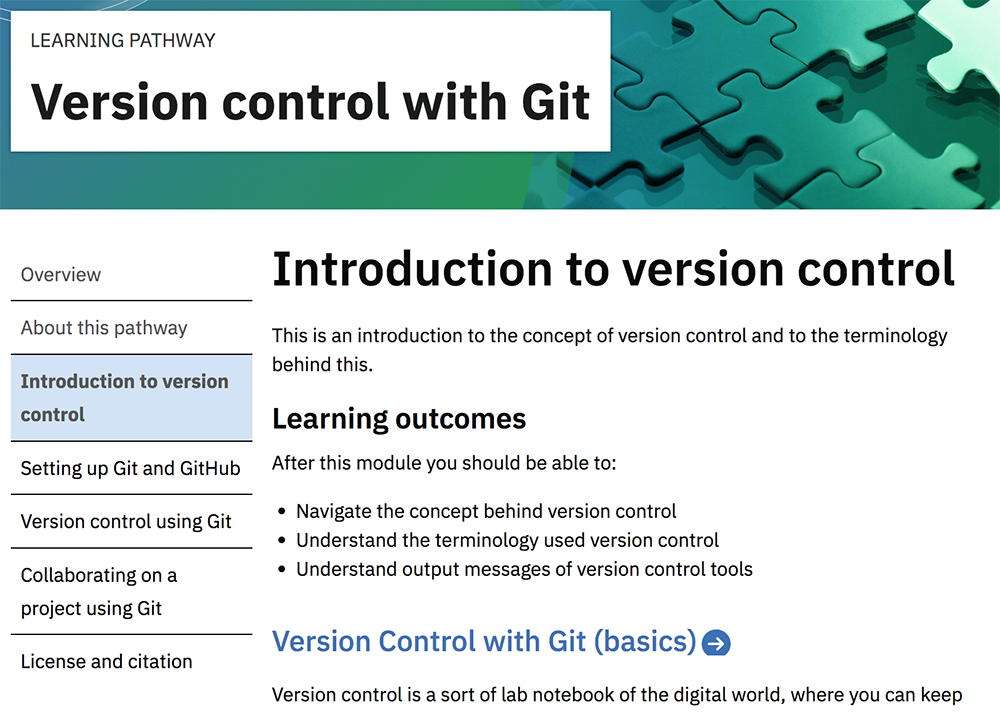
Learning pathways are developed within the framework of the hub. The pathways are collections of training courses and materials to help researchers learn about specific topics. For example, PDC has just released a course on “Version control with Git” (see cms.competency.ebi.ac.uk/learning-pathway/version-control-git ). Through this pathway, researchers can learn about version control, which is the practice of tracking and managing changes to software code. The aim of the course is to give an indication of the level of complexity of the computational techniques and knowledge required to keep track of what a developer did and when, and also to demonstrate how to work collaboratively on a document or contribute actively to an open-source project.
Together with BioExcel, PDC co-organised the online “Introduction to HPC for Life Scientists” course hosted by Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC). There Szilárd Páll (PDC) and Berk Hess (KTH) gave a collection of inspiring lectures and exercises on “Mapping computation to HPC hardware and GPU accelerators and heterogeneous architectures” (see permedcoe.eu/training_type/material ). The workshop was a significant success, with remarks from the participant such as “The course has opened my eyes to the potential of HPC in my research field” and “Gaining hands-on experience with GROMACS and PhysiCell has given me the confidence to optimise my research projects for HPC environments”.
Finally, PDC is undertaking a performance and scalability analysis of different workflows for Personalised Medicine on the Dardel supercomputer system at PDC. These workflows are designed to solve different PerMed use cases ( permedcoe.eu/use-cases ) which tackle real-life medical problems, such as multiscale modelling of the COVID-19 virus and drug synergies for cancer treatment. In particular, Xavier Aguilar (PDC) has been looking at the types of problems that workloads face when they run on a high number of cores, for example, communication problems across nodes, work imbalances, or memory contention issues within a node. In addition, Xavier is exploring the challenges of deploying multiscale workloads in an optimal manner on an HPC infrastructure such as Dardel, since these are not the common monolithic parallel HPC codes.